Build serverless system with Pulumi and AWS (Part 2)
By Yves Denis Deffo
Introduction
In our previous article, we focused on the lambda-Sync part of our serverless system which corresponds to the synchronous part of our application.
We had already set up our entire continuous integration pipeline consisting of Github for the VCS, Codebuild to build our docker images and finally Cloudformation to deploy our resources in the AWS environment.
For this second part, there is no need to reinvent the wheel. We will use the instruments already in place and implement our asynchronous circuit.
The full source code of this project
Functional requirements
- The application should expose an endpoint to create an order item.
- The Create operation should be asynchronous. The response status code is 204 for a successful operation.
- The Create operation should insert an order record in the database.
- Once an order is registered in the database, it must go through the payment process and eventually be sent to a restaurant. If the payment process is successful, the order can be sent to a restaurant, in this case the end user should receive an email with the status of the transaction.
Architecture diagram
For this part , we deployed new aws resources through Cloudformation : SQS , SNS , Stepfunctions
SQS
AWS SQS is a message queue service used by distributed applications to exchange messages through a polling model, and can be used to decouple sending and receiving components. In case of high rate of create operations, it helps us to buffer orders in the queue so that our lambda services are not overwhelmed. it’s a serverless system so it’s fully managed and automatically scales.
In case of failure while procssing a message , we set up a Dead letter queue which is another queue which recives only problematic messages.
##########################################################################
# SQS QUEUE AND DLQ #
##########################################################################
OrderQueue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
Properties:
QueueName: "OrderQueue"
RedrivePolicy:
deadLetterTargetArn: !GetAtt [OrderDLQueue,Arn]
maxReceiveCount: 3
OrderDLQueue:
Type: AWS::SQS::Queue
Properties:
QueueName: "OrderDeathLetterQueue"
To integrate this queue with ApiGateway we add a new resource api as is :
post:
consumes:
- "application/json"
produces:
- "application/json"
responses:
"201":
description: "201 response"
x-amazon-apigateway-integration:
type: "aws"
credentials:
Fn::GetAtt: [ ApiGwExecutionRole, Arn ]
httpMethod: "POST"
uri:
Fn::Sub: arn:aws:apigateway:${AWS::Region}:sqs:path/${AWS::AccountId}/${OrderQueue.QueueName}
responses:
default:
statusCode: "201"
requestParameters:
integration.request.header.Content-Type: "'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'"
requestTemplates:
application/json: "Action=SendMessage&MessageBody={\"data\":$input.json('$')}"
passthroughBehavior: "when_no_match"
For the Post request, our apigateway will send the response body to OrderQueue. At line 79 the content type must be application/x-www-form-urlencoded and at line 81 we defined the message body of the sqs event.
Stepfunctions
AWS Step Functions is a serverless orchestration service that lets you integrate with AWS Lambda functions and other AWS services to build business-critical applications. It consists of three main components such as State machines , States and Task states.
In our case it helps us orchestrate 3 different lambdas by managing the order management workflow. The state machine definition used for this project is here
We add this config in our Cloudformation template :
##########################################################################
# STEPFUNCTIONS #
##########################################################################
OrderStateMachine:
Type: AWS::Serverless::StateMachine
Properties:
DefinitionUri: ./stepfunctions/order.asl.json
DefinitionSubstitutions:
ManageOrderStateArn: !GetAtt ManageOrderStateFunction.Arn
ProcessPaymentArn: !GetAtt ProcessPaymentFunction.Arn
SendOrderArn: !GetAtt SendOrderFunction.Arn
Policies:
- LambdaInvokePolicy:
FunctionName: !Ref ManageOrderStateFunction
- LambdaInvokePolicy:
FunctionName: !Ref ProcessPaymentFunction
- LambdaInvokePolicy:
FunctionName: !Ref SendOrderFunction
- Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action:
- cloudwatch:*
- logs:*
Resource:
- "*"
Logging:
Destinations:
- CloudWatchLogsLogGroup:
LogGroupArn: !GetAtt OrderStateMachineLog.Arn
IncludeExecutionData: true
Level: 'ALL'
OrderStateMachineLog:
Type: AWS::Logs::LogGroup
Properties:
LogGroupName: !Join ["/", ["stepfunctions",OrderStateMachine]]
…which results to this graph view in the AWS console:
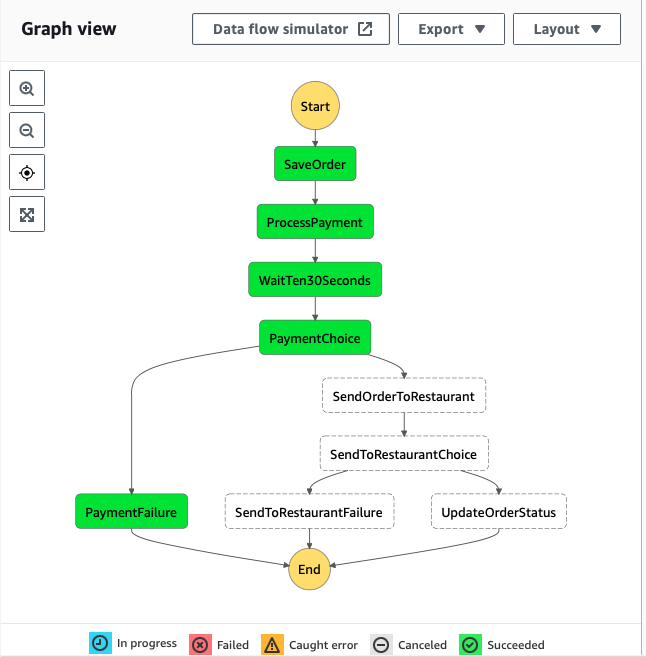
As seen in the figure above , the workflow starts with the task Save Order implemented by the manage state service, it will save the order in the dynamodb table.
The next step is the process payment executed by payment process service which will randomly decides whether the payment status is ok or not.
After the payment process, the workflow will pause for 30s and afterwards makes a choice based on th payment status:
- If the payment is ok , the order will be sent to the restaurant.
- If the payment is not ok, the state machine will end the workflow. In both cases the order status is updated in the database.
SNS
AWS SNS is a managed messaging service for communication, allowing messaging between decoupled microservices applications or directly to users with SMS or Email. It’s used in this project to send notification about the order status to the end user who creates the order.
##########################################################################
# SNS TOPIC #
##########################################################################
OrderSnsTopic:
Type: AWS::SNS::Topic
Properties:
Subscription:
- Endpoint: !Ref UserEmail
Protocol: "email"
TopicName: "Order-sns-topic"
PS: Once Cloudformation will deploy this resource , the owner of the email address will receive an subscription confirmation email from AWS.
Integration test
Let’s try to create an order by making a post request to the apigateway(from command line):
-- Request:
curl --location --request POST 'https://xxxxxx.execute-api.ca-central-1.amazonaws.com/Dev/orders/' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"user_id": "Burger_20",
"quantity": "3",
"restaurant_id": "Restaurant 4"
}'
-- Response:
{"SendMessageResponse":{"ResponseMetadata":{"RequestId":"80d9961e-2514-5879-97b4-ca207d6766ef"},"SendMessageResult":{"MD5OfMessageAttributes":null,"MD5OfMessageBody":"e172a0b1b0c410a6d12b96ef434aa4c0","MD5OfMessageSystemAttributes":null,"MessageId":"603cdde2-74aa-4233-aac0-ec02a3160103","SequenceNumber":null}}}
Ok , let’s take a look at the Dynamodb table:
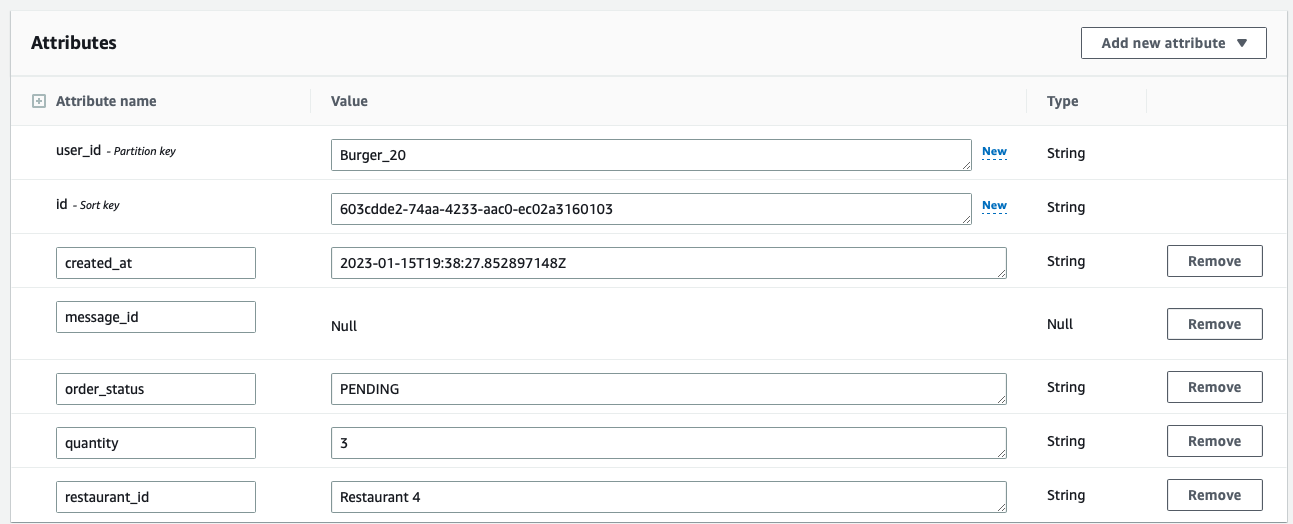
…And we just receive an email notification from sns:

Et Voila! 😃
Conclusion
For the second part , we implemented the async process of order management with sqs, sns and stepfunctions. Those are resources heavily used in real world scenarios so it’s important to know are they work independently and together. For the next step , we’ll need to secure our apigateway endpoints with an AWS authentication resource called Amazon Cognito so stay tuned… 😉
